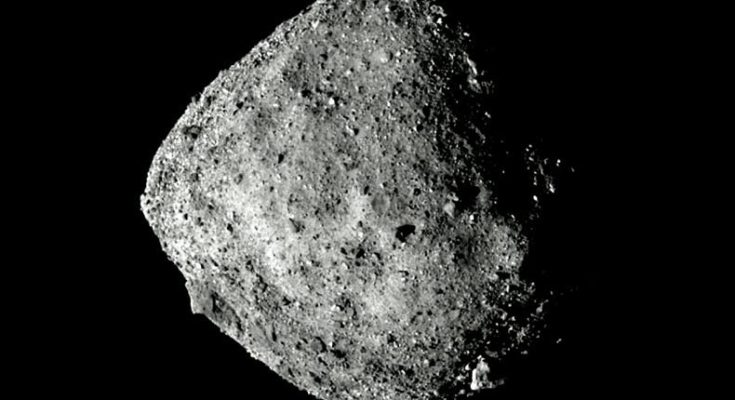
Giant asteroid to hit the Earth in 2019. Image Courtesy – Daily Express
A panic has been surrounded in the world that a huge asteroid could hit this year. News from various sources published over the last couple of days informing us that we are about to collide with a huge piece of rock that could make havoc damage on the earth.
A space agency warns that Huge 164-foot asteroid could collide into the earth with a velocity of 27,400 mph; flatten area of the asteroid is bigger than London.
Another report of the European Space Agency has been published, mentioning that the asteroid of class 2006 QV89 is the 4th most dangerous space object according to their list. But, it is notable that expectation is there to collide with the earth – though the list of the agency is known as ‘risk list’. We can assume that although there are risk factors to hit the earth, still the probability is low. When it will actually arrive, it will surely pass by the Earth at a distance that could be nearly more than thousand miles.
Read: Monstrous supernova in the sky surpassing all the earlier records
NASA’s asteroid trackers informed that a 2700 megatons of TNT explosive like asteroid is going to hit the earth in the month of October this year. The asteroid named FT3 is a monstrous space object with a diameter of 1115 ft. If it collides with the Earth with a velocity of 20.37 km/sec. or more than 45, 500 mph, the impact would be like 270,00,00,000 tonnes of TNT.
After this estimation, NASA also analyzed a low probability of hitting the Earth on 2nd October 2024 and then on 3rd October 2025. The asteroid FT3 is following the same orbit of asteroid 1862 Apollo, and it circles the Sun within the ‘Asteroid Belt’ in between Mars and Jupiter.
NASA is actively working to prepare a defence mechanism to avoid from a possible collision, or to divert the asteroid somehow from its track.
NASA is continuously conducting space and aeronautics research with analyzing planetary system, the Sun and the Moon, asteroids and other space objects. NASA has selected eight new research teams to cooperate with research studies around the space and named the task as ‘Solar System Exploration Research Virtual Institute’ (SSERVI).