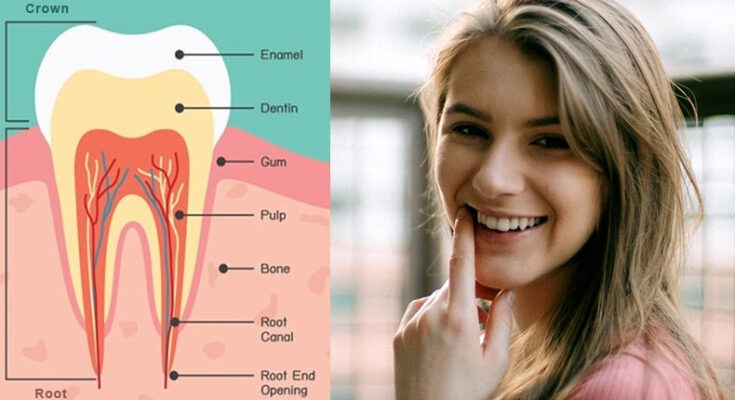
Modern way of tooth engineering with remineralization. Image Courtesy – Teeth Talk Girl
The worldwide frequency of dental caries and sensitivity has amplified over the last two eras. This has led to augmented importance in emerging improved treatments. Dental caries is a bacterial infection that results in the advanced dissolution and loss of tooth minerals, called demineralization.
While, remineralization is defined as the method whereby calcium and phosphate ions are provided from a source external to the tooth to advance ion deposition into crystal vacuums in demineralized enamel, to deliver a mineral gain. It is one of the most promising healing strategies for the replacement of the unhealthy damaged tooth.
In recent times, a variety of novel calcium-phosphate-based remineralization delivery methods has been developed in the medical application; magnetic field exposure is one of them. Gels made of casein phosphopeptide – amorphous calcium phosphate blended with nano chitosan were utilized as an external source and combined with the exposure of the tooth surface to a magnetic field of 1.8mT for 20 min. Fluoride; typically sodium fluoride is a well-recognized remineralization agent that supports the remineralization of caries when released into saliva from oral care products.
This remineralization method has been researched and a lot of them are being used clinically, with considerably predictable positive results. Along with the previous techniques stem, cell-mediated tissue regeneration is a new approach for regenerative medicine of human teeth. Doctors relocated both human SCAP and periodontal ligament stem cells to generate a root capable of supporting a porcelain crown, resulting in normal tooth function. This hybridized engineering method led to the recovery of tooth strength and appearance.
Read: New technology for tooth rejuvenation will come very soon
Current advances in dental stem cell biotechnology and cell-mediated murine tooth regeneration have empowered scientists to investigate the potential for regenerating existing teeth. Murine teeth can be regenerated by a few distinctive stem cells to cooperatively form dental structures. However, due to the difficulty of human tooth growth and development, the regeneration of a whole tooth structure including enabling, pulp complex, and periodontal tissues as a useful unit in humans not possible with available regeneration biotechnologies.
Dental implant treatments also have attained lasting achievement in the surgery for the recovery of tooth function. Reform of teeth in patients without adequate jawbone support would be a key advance. In addition to this, stem cell-mediated root generation offers opportunities to recover a bio-root and its associated tissues.
The great developments in computing-related technologies and materials have broadened the choices to alternative and more accurate dental treatments and aided in establishing more consistent diagnostic tools and therapeutic strategies. The above-mentioned progressions have been made with the arrival of novel technologies such as computer-aided design and manufacturing technology, digital radiography, and computer-supported implant surgical procedure.
In all recent technologies, the most significant improvement of the last decade is the augmentation of stem cells technology to repair or regenerate numerous damaged tissues. Stem-cell-based regenerative is related to advanced tissue engineering products which have formed a vital medical change toward the useful repair and regeneration of damaged dental tissues. This development holds great promise for the growth of well-organized and bespoke treatments shortly.